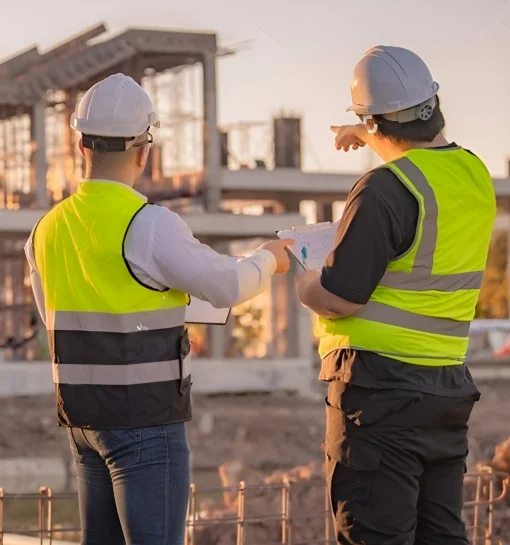
Special Inspection
What is Special Inspection?
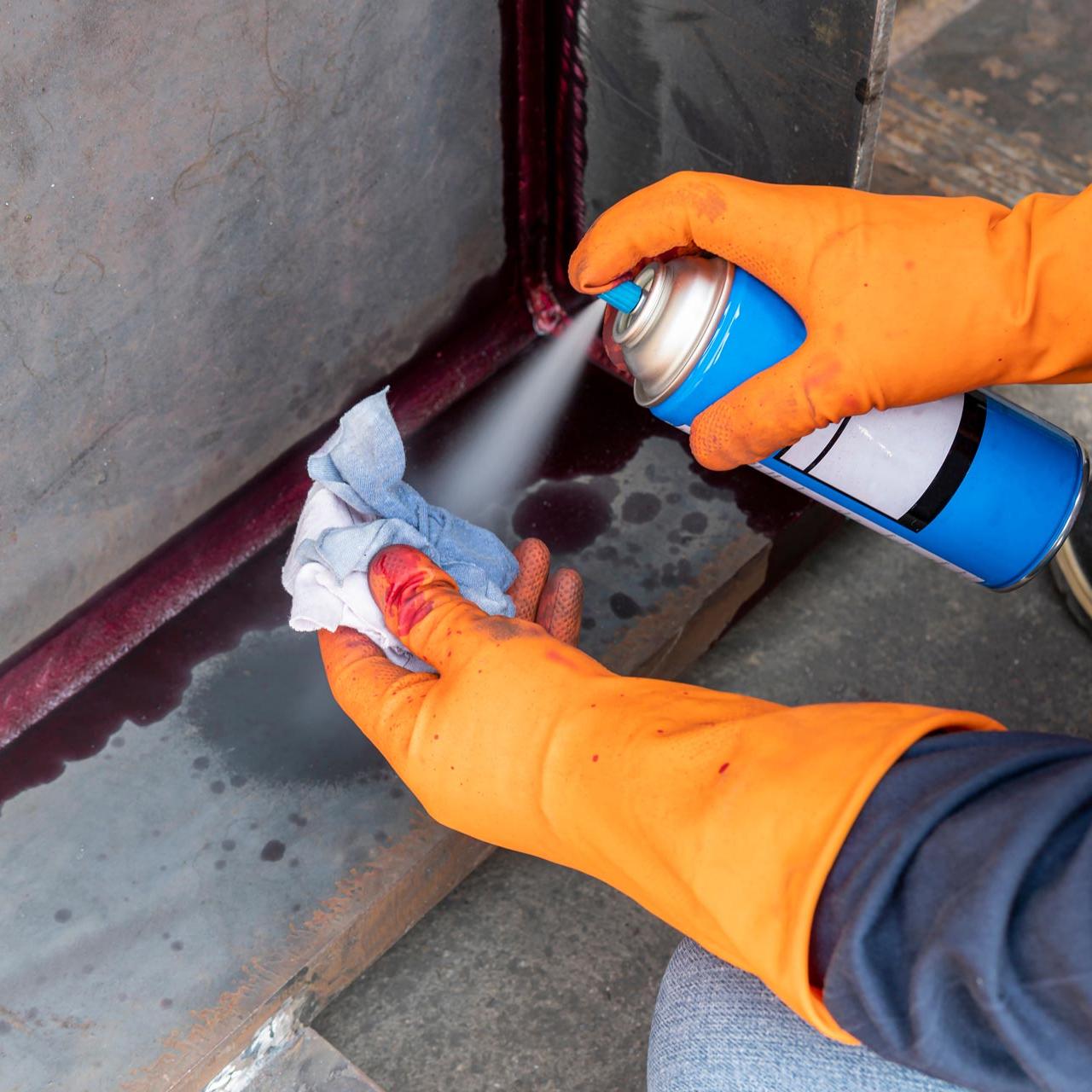
Special Inspection in New York City refers to a process mandated by the NYC Building Code that requires specific inspections to be performed by qualified inspectors for certain aspects of construction and building work. These inspections are designed to ensure that the work complies with approved plans, applicable codes, and regulations, thereby promoting safety and quality in construction.
Why Do I need Special Inspection Services?
Special inspection services are essential for several reasons, particularly in the context of construction and building projects. Here are some key reasons why you might need special inspection services: Compliance with Regulations, Quality Assurance, Safety, Risk Mitigation, Enhanced Credibility, Final Approval and Occupancy, Peace of Mind and Long Term Value.
Who Performs Special Inspections?
Special inspections are performed by qualified professionals known as special inspectors. These inspectors are typically associated with a Special Inspection Agency (SIA) that is approved by the relevant local building authority, such as the NYC Department of Buildings in New York City.
When are Special Inspections required?
Special inspections are required at various stages and for specific types of construction work, primarily to ensure compliance with building codes and standards. Below are some scenarios when special inspections are typically mandated:
- Concrete work (e.g., cast-in-place concrete, precast concrete)
- Steel construction (e.g., welding, bolting)
- Masonry (e.g., brick, block, stone)
How do I schedule a Special Inspection?
Scheduling a special inspection involves a few key steps to ensure that the process is organized and compliant with local regulations. Here’s a general outline of how to schedule a special inspection:
- Engage a Special Inspection Agency (SIA)
- Develop a Special Inspection Plan (SIP)
- Submit the SIP for Approval
- Coordinate with the Construction Schedule
- Schedule the Inspections
- Prepare for the Inspections
- Conduct the Inspections
- Review and Follow Up
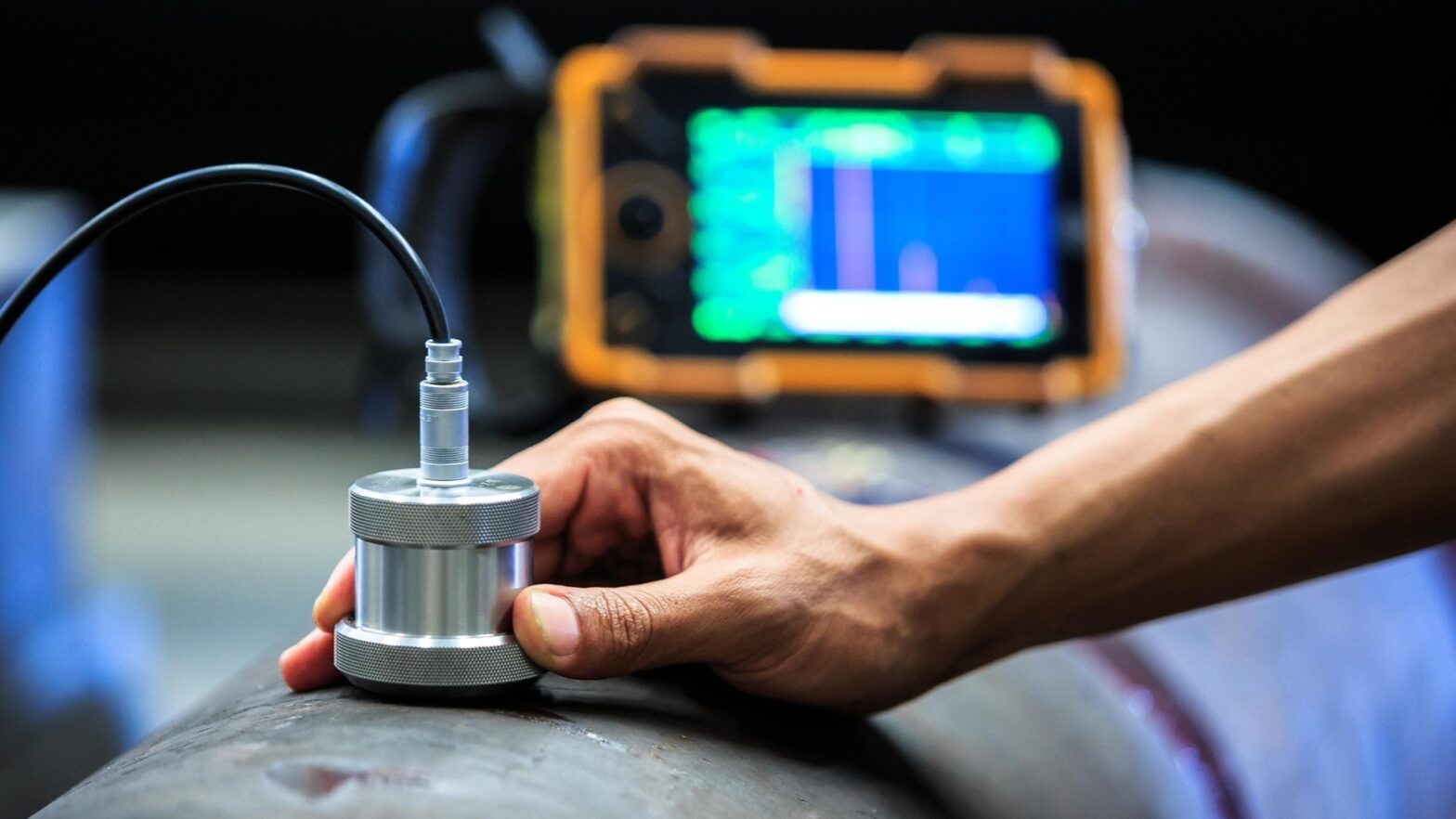
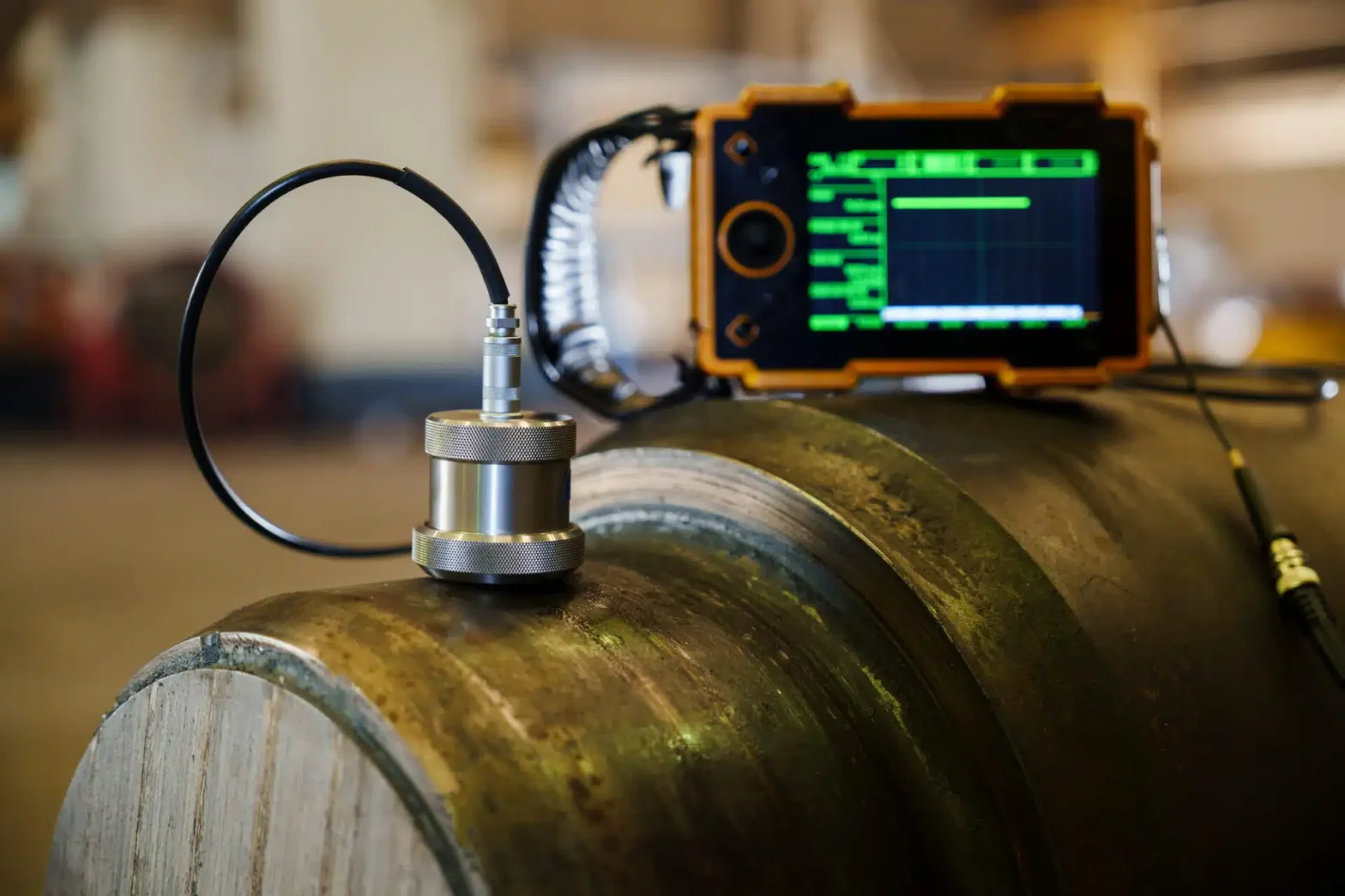
Materials Testing
What is Materials Testing?
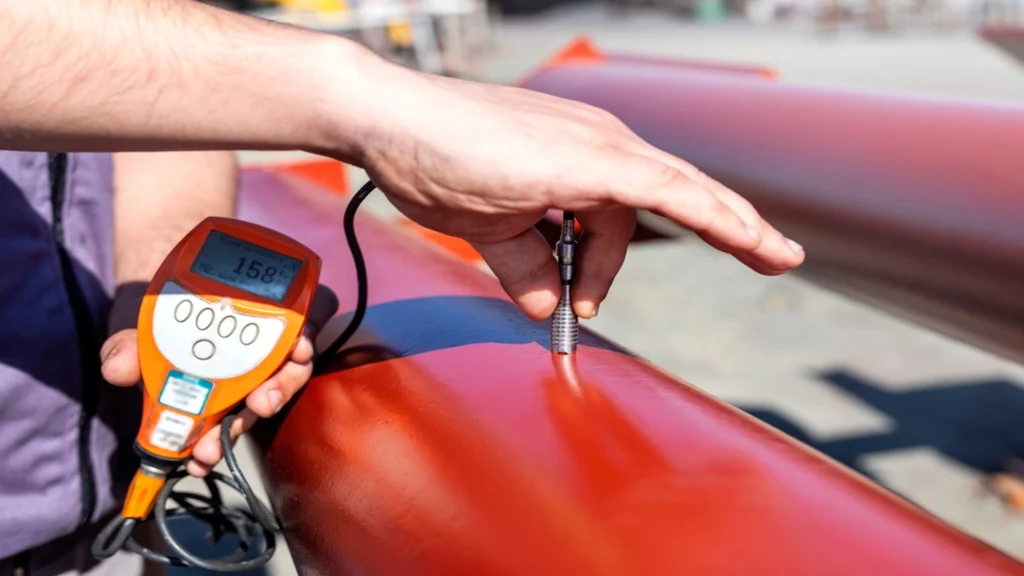
Materials testing is a critical process in construction and engineering that involves evaluating the physical and chemical properties of construction materials to ensure they meet specified standards and requirements. This testing helps determine the suitability of materials for their intended use, ensuring safety, performance, and quality in construction projects.
Why is Materials Testing important?
Materials testing is crucial for several reasons, particularly in the fields of construction, engineering, and manufacturing. Here are some key points highlighting the importance of materials testing:
- Safety Assurance
- Quality Control
- Compliance with regulations
- Performance Evaluation
- Durability Assessment
- Cost Efficiency
- Material Selection
- Innovative Solutions
- Risk Mitigation
- Client Confidence
What types of materials can be tested?
A wide variety of materials can be tested in construction and engineering to ensure their suitability for specific applications. Here are some of the main types of materials that can undergo testing:
- Concrete
- Soil
- Steel
- Asphalt
- Aggregates
- Wood
- Bricks and Masonry
- Insulation Materials
How are materials samples collected for testing?
The collection of material samples for testing is a critical process in construction and engineering, ensuring that the materials used in a project meet required standards and specifications. The methods for sample collection can vary depending on the type of material being tested.
How long does it take to get test results?
The time it takes to receive test results for materials can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of material being tested, the specific tests being conducted, the complexity of the analysis, and the laboratory’s workload. Here’s a general overview of the timelines for various materials:
- Concrete:
- Compressive Strength Tests: Typically, results are available in 24 to 48 hours for standard curing tests, but full strength results may take 28 days.
- Other Tests: Additional tests may take several days to weeks, depending on the type.
- Soil:
- Basic Tests (e.g., moisture content, density): Results can often be provided within a few days.
- Comprehensive Tests (e.g., shear strength, consolidation): These may take one to two weeks or longer, depending on the complexity.
- Steel:
- Tensile and Yield Strength Tests: Results are generally available within a few days to a week.
- Other Tests: Additional testing may require longer periods, especially if more complex analyses are needed.>
- Asphalt:
- Basic Tests (e.g., density, viscosity): Results can usually be obtained within a few days.
- Complex Tests: More detailed analysis can take one to two weeks.
- Aggregates:
- Gradation and Cleanliness Tests: Results are typically available within a few days.
- Other Tests: Depending on the analysis, additional tests may take longer.
Monitoring
What does the Monitoring service entail?
Construction monitoring is a service that involves the systematic observation and assessment of construction activities in a project site to ensure compliance with project specifications, safety standards, and regulatory requirements. This service is typically provided by qualified professionals, such as construction managers, project managers, or third-party inspectors.
Monitoring application could either be within the construction or jobsite to ensure the safety of workers, equipment and materials; or, to adjoining structures within the area of influence of the activity to safeguard it from damage and to ensure the safety of its occupants or users
What types of projects require Monitoring?
The types of project require monitoring are:
- Building Construction
- Excavation and Earthworks
- Piling and Foundation Work
- Bridge Construction and Repair
- Tunnelling and Underground Construction
- Demolition
- Road and Rail Construction
- Heavy Machinery Operations
- Industrial Facilities
- Geotechnical Investigations
- Historic Preservation
- Oil and Gas Exploration
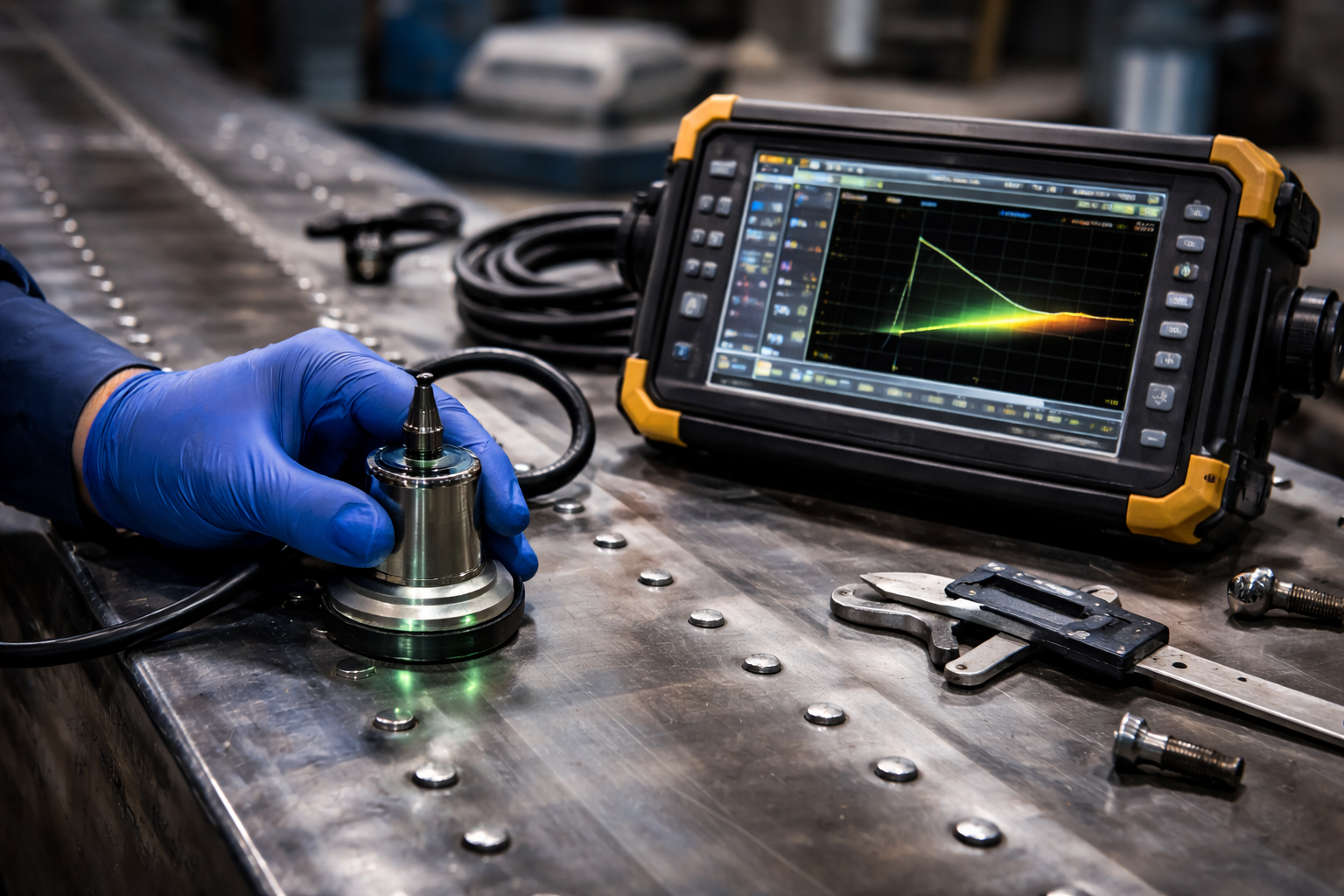
What Technologies are used in Monitoring?
Construction/Foundation Monitoring involves the use of various technologies and methods to assess the condition and performance of foundations over time. These technologies help detect movement, settlement, and other structural changes that may affect the integrity of a building or structure. Here are some common technologies used in foundation monitoring:
- Vibration Monitors
- Optical Monitoring (AMTS)
- 3D Laser Scanning
- Inclinometers
- Settlement Plates
- Piezometers
- Strain Gauges
- Geotechnical Sensors
- Load Cells
- Remote Sensing Technologies: LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- Drones
- Data Acquisition Systems
Quality Control Laboratories, LLC. can perform these monitoring Services:
How often is monitoring Conducted?
The frequency of monitoring for foundation and structural conditions can vary based on several factors, including the type of project, the specific monitoring technology used, the potential risks involved, and any regulatory requirements.
How are Monitoring results reported?
Monitoring results for foundation and structural conditions are typically reported through a structured process that ensures clear communication of findings, observations, and recommendations. Here are the common components and methods used to report monitoring results:
- Regular submission of reports
- Content Reports: eg. Executive Summary, Methodology, Data Presentation, Observation, Comparative Analysis, Recommendation
- Final Reports


 Contact Us
Contact Us 














 View Opportunities
View Opportunities